Innovative Strategies and Risk Management in Pistachio Production: From Regulated Deficit Irrigation to the Role of Genetics and IoT
1. Introduction: The Paradigm Shift from “More Water” to “Smart Water”In the face of ongoing climatic change and water scarcity, focusing solely on the total volume of water consumed is insufficient. The critical benchmark for the pistachio industry’s survival is the “quantity of quality yield per unit of water consumed,” also known as Irrigation Water Use Efficiency (WUE_i). Traditionally, farmers operated under the assumption that more water equals a higher yield. Today, the science of sustainable agriculture proves that through precise management strategies, crops can be produced with suitable yield and quality using less water. This article explores the two main pillars of this new paradigm: Management Techniques (RDI) and Technological Innovations (IoT and Genetics).

2. Management Techniques: Regulated Deficit Irrigation (RDI)Regulated Deficit Irrigation (RDI) is a sophisticated management practice where trees are intentionally subjected to a specific level of water stress, but only during certain non-critical phenological stages.2.1. Precision Timing and ImplementationThe pistachio tree’s annual growth cycle has distinct phases with varying sensitivities to water stress: * Critical Stages (Full Irrigation Required): * Bud swell and flowering stage (Spring). * Nut filling stage (Mid-summer). * Non-Critical Stages (RDI Applicable): * Rapid shoot growth phase (Early summer). * Post-harvest until dormancy begins (Late summer/Autumn).> RDI Advantage: By applying controlled water stress during non-critical periods, farmers achieve significant water savings (up to 20-30\%) without a proportional, negative impact on final yield or quality. In some cases, RDI can even be managed to enhance nut quality metrics.>
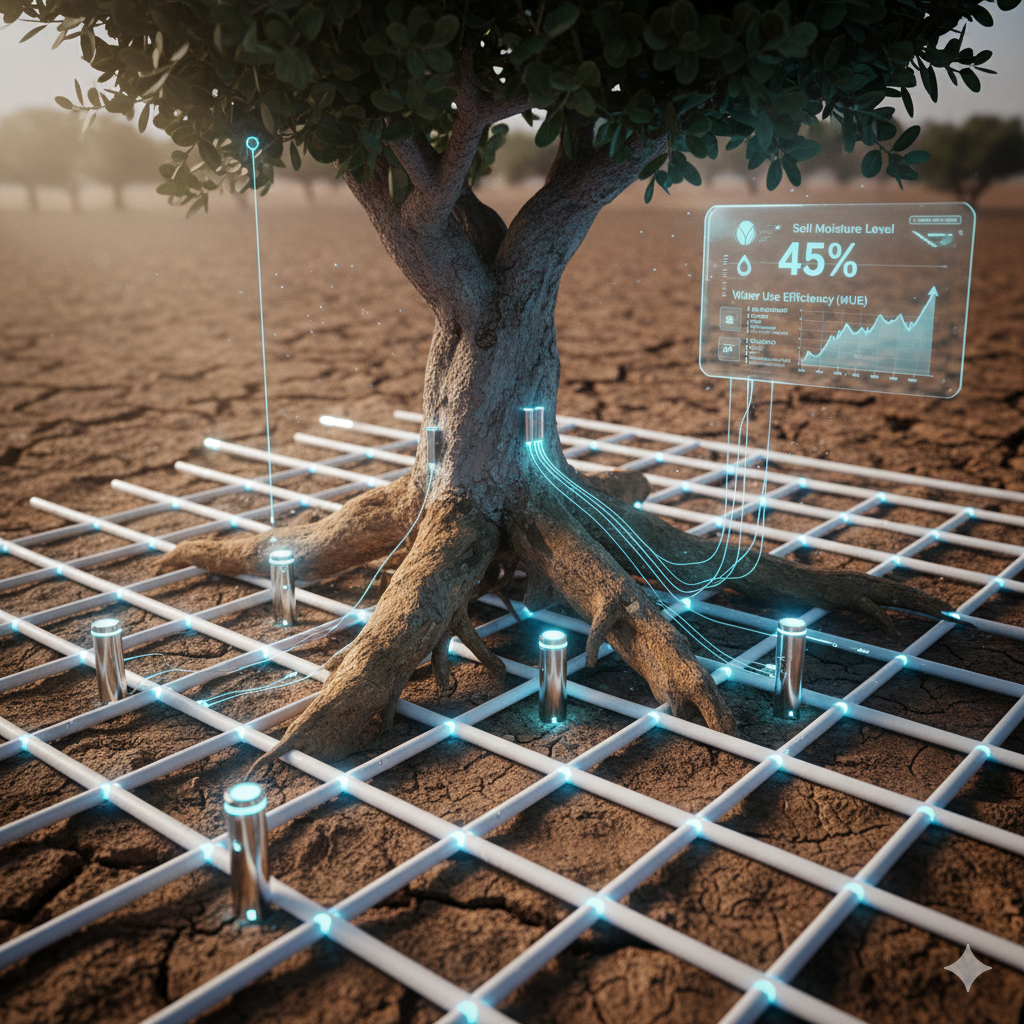
3. Technological Innovations: The Smart Farming RevolutionModern technologies play a crucial role in the accurate and scientific execution of RDI. Traditional irrigation scheduling (based on a fixed calendar or simple estimation) carries high risks under drought conditions.3.1. The Role of the Internet of Things (IoT) and SensorsInstalling soil moisture sensors at various depths allows the farmer to gauge the tree’s actual needs instead of relying on guesswork. These IoT-enabled sensors transmit real-time data to a central platform. * Practical Application: The system alerts the farmer precisely when the soil moisture dips below the threshold, indicating the exact timing and necessary volume for irrigation. This prevents water wastage caused by over-irrigation.
3.2. Aerial Imagery and Data AnalyticsUsing multispectral cameras mounted on Drones or utilizing satellite imagery, the health of the tree canopy can be assessed using indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index). These images identify areas under water stress or pest infestation in their early stages, allowing the farmer to apply water or treatments only where needed (Precision Agriculture).4. Long-Term Risk Management: Pistachio GeneticsThe ability of a pistachio tree to resist salinity and drought is a fundamental genetic trait. The strongest long-term solution involves embracing plant breeding science: * Developing Resistant Rootstocks: Researchers are working to identify, select, and propagate pistachio rootstocks (the root and lower stem portion of the tree) that demonstrate high tolerance to soil salinity and water scarcity. Grafting high-yield commercial varieties (like Akbari and Ahmad-Aghaei) onto these resilient rootstocks can significantly enhance the orchard’s sustainability in regions with saline or limited water.

- Targeted Genetic Improvement: Utilizing advanced genetic techniques to accelerate the breeding process and develop cultivars that can maintain yield and kernel quality with reduced water input, securing a more climate-resilient crop for the future.
- Conclusion: Pistachio, the Future Crop with a Smart Approach
The survival of Iran’s pistachio industry depends on its capacity to recognize that water is a finite resource. Pistachio can be a “water saver,” provided that farmers and policymakers integrate traditional agriculture with technology and water management science. Successful implementation of RDI, adoption of IoT, and investment in genetic improvement represent the roadmap for transforming the pistachio from a high-risk crop into a strategic, smart, and sustainable commodity in the water-scarce economy of Iran.
Contact and Ordering Information
For further information, consultation regarding bulk pistachio purchases, or to place an order, please contact Mr. Ravanshad via WhatsApp:
📞 WhatsApp: 00989214773705

